I have been busy dealing with jQuery lately with a project in hand which has given me a lot of hands on with jQuery. Therefore, I would like to share some of the things I came across when I was working with jQuery. If you still confuse what i am talking about you may want to visit my previous post on jQuery.
1. jQuery id and class selector.
jQuery selector can only selects one id but is able to select multiple classes. For example, you have a multiple id with the same name,
<div id='sameid'></div> <div id='sameid'></div>
with a declaration of selector as follow,
$('div#sameid')
jQuery will only retrieve the first id it sees. However, if your declaration is a class instead of id,
<div class='sameid'></div> <div class='sameid'></div>
with a declaration of selector as follow,
$('div.sameid')
it will provide you with a set of jQuery object that contains the two object above.
2. jQuery animation lag during hover on multiple objects.
jQuery has an event 'hover' which act exactly similar to 'hover' in CSS. However, when we try to render hover on multiple set of elements, an animation lag may occur that doesn't seem smooth. This may be a problem with the way the code has been written. Let me show you what i meant here, take a look at playgroundblues.com, notice they have a nice navigation bar on the left hand side which display nicely on the left corner. The problem with this navigation bar is when you try to move very fast across the multiple objects several times, you will notice the animation continues to perform although your hover has already ended.
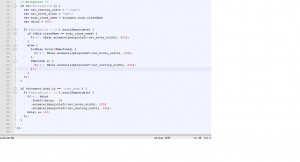
If we look at his code written for the menu,
You will notice that there are two selector of $('#navigation > li') where one assign the hover function while the other perform the nice welcome sliding when visitor enters their side. There are no problems with the logic on the code above but because the codes for animation are being separated to two assignments, it created the lag during the animation. If all the assignment is done on a single selector of $('#navigation > li') through chaining, the animation lag will be eliminated.
3. $(this) and 'this' .
Often enough i find myself getting confuse with when to use $(this) and 'this' in jQuery. The differences are $(this) refers to ALL jQuery objects while 'this' refers to the calling object in javascript. For example, we want to use .each and fadeIn() of jQuery after a selector such as below,
$('div#product').each(function(){
$(this).fadeIn()
})
since fadeIn() is a jQuery effect function, we use $(this) but if we are not dealing with jQuery objects we used 'this' instead.
$('div.product').each(function(){
var myClass = this.className; // provided you have multiple class product
})
The reason why 'this' can be used here is due to the function of jQuery .each which look into each DOM object. Simple to say, this refer to the normal DOM object while when you have the extra $(xxxx), it will refer it to a jQuery object which allows you to use jQuery method.
4. find() function in jQuery
Being a forgetful person (which is why i have this blog), i often find myself forgetting what does the code $('a', this) in jQuery means. It basically means, find anchor object in 'this'. It is just a shortcut for jQuery to subsitute find () method.
5. ',' in jQuery selector.
You may have a chance to see $("div#idx, div#idc") and confuse got confuse with it as this doesn't look like anything on the api of jQuery! It is just another quick function in jQuery to do a selector in a single declaration instead of multiple statement. The ',' comma represent the 'OR' condition which is similar to '||' in java or javascript. So the selector i wrote means "select div with id idx or div with id idc".
That is all I can remember from what had happen during my coding with jQuery. If there are any more tips that I have come across during my coding, i will update here! Hope these helps! Cheers!