This is something pretty short and useful for many mysql InnoDB users. Pretty much you will come across optimizing MySQL InnoDB due to performance issues or MySQL is causing a lot of 'slow' sql queries throwing in your way. Of course, there are pros and cons in doing every type of optimisation such as sacrificing reliability and etc.
MySQL InnoDB Configuration
Before i began explaining what the heck did i do, if you are lazy and just wish to try out whether my configuration works, just head over to your MySQL my.cnf file in /etc/my.cnf and place this on [mysqld]
P.S: this is a linux configuration
[mysqld] innodb_flush_method=O_DIRECT innodb_lock_wait_timeout=1 innodb_autoextend_increment=512 innodb_io_capacity = 100 innodb_thread_concurrency = 32 innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2 innodb_read_io_threads = 32 innodb_write_io_threads = 32 innodb_buffer_pool_size=400M innodb_file_per_table=1 innodb_stats_on_metadata=0
The above configuration will most likely helps to smoothed out most of your InnoDB problens. Especially if you are getting a 10-50 seconds for MySQL slow log.
MySQL InnoDB Configuration Explanation
Now let's go through one by one and explain what each does.
innodb_flush_method
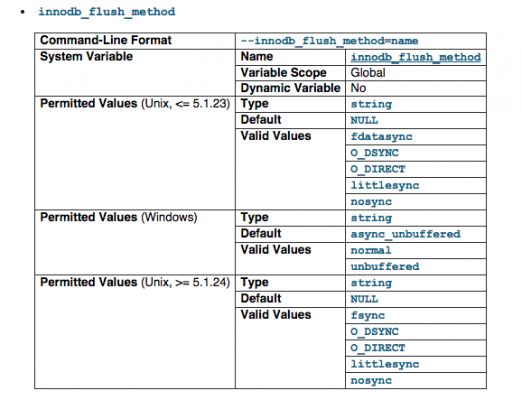
innodb_flush_method defines the method used to flush data to the InnoDB data files and log files, which can affect I/O throughput. If you look at the image, the default value is NULL, and we have changed it to O_DIRECT to better control I/O throughput. We basicall still using fsync but only for write. read we will use a O_DIRECT instead of fsync. If you are interested to more head over to stackoverflow
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_flush_method
innodb_lock_wait_timeout
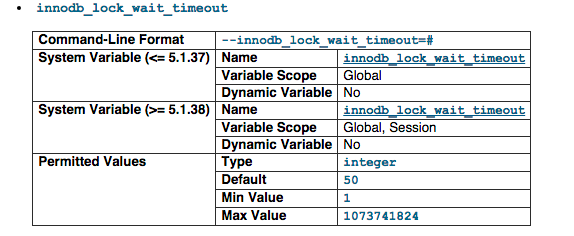
The timeout in seconds an InnoDB transaction waits for a row lock before giving up. The default value is 50 seconds. A transaction that tries to access a row that is locked by another InnoDB transaction waits at most this many seconds for write access to the row before issuing an error. We have set it 1 seconds as this is the only time we can wait for a row being lock or we will just fail the transaction if not we will have a pile of long queue in a busy server.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_lock_wait_timeout
innodb_autoextend_increment
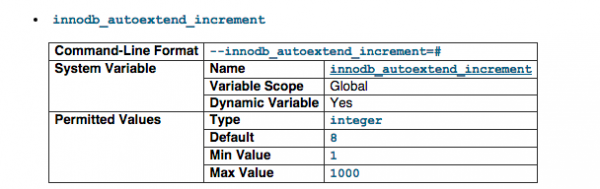
The increment size (in MB) for extending the size of an auto-extending shared tablespace file when it becomes full. Mainly for sharding setting
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_autoextend_increment
innodb_io_capacity
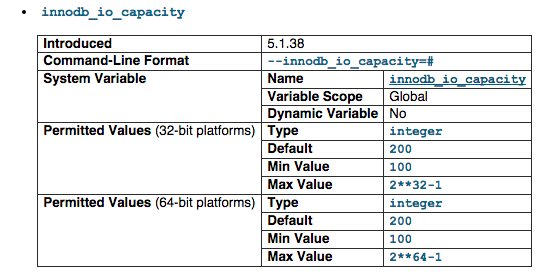
An upper limit on the I/O activity performed by the InnoDB background tasks, such as flushing pages from the buffer pool and merging data from the insert buffer. The default value is 200. For busy systems capable of higher I/O rates, you can set a higher value at server startup, to help the server handle the background maintenance work associated with a high rate of row changes. For systems with individual 5400 RPM or 7200 RPM drives, you might lower the value to the former default of 100.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_io_capacity
innodb_thread_concurrency
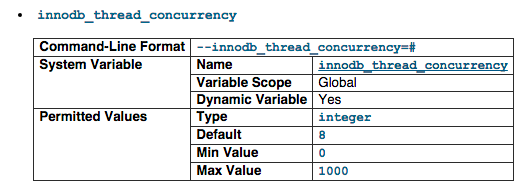
InnoDB tries to keep the number of operating system threads concurrently inside InnoDB less than or equal to the limit given by this variable (InnoDB uses operating system threads to process user transactions). Once the number of threads reaches this limit, additional threads are placed into a wait state within a “First In, First Out” (FIFO) queue for execution. Threads waiting for locks are not counted in the number of concurrently executing threads.
We have 32 CPU, hence, the 32 value. But you can lower this to ensure that it doesn't suck up all the resources.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_thread_concurrency
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit
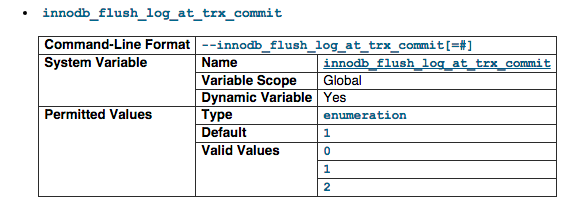
If the value of innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit is 0, the log buffer is written out to the log file once per second and the flush to disk operation is performed on the log file, but nothing is done at a transaction commit. When the value is 1 (the default), the log buffer is written out to the log file at each transaction commit and the flush to disk operation is performed on the log file. When the value is 2, the log buffer is written out to the file at each commit, but the flush to disk operation is not performed on it.
Basically we are trying to tell InnoDB to not work too hard by setting it to '2'.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit
innodb_read_io_threads
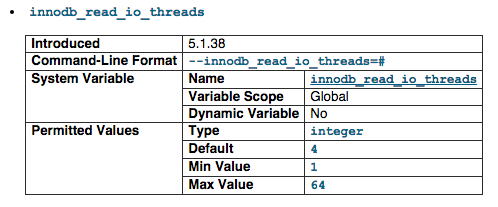
The number of I/O threads for read operations in InnoDB. The default value is 4. We set it to 32.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_read_io_threads
innodb_write_io_threads
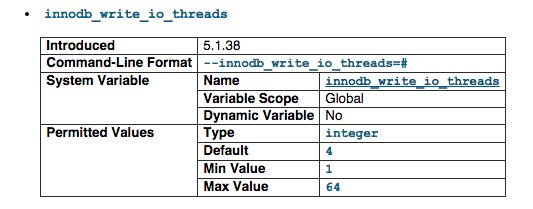
The number of I/O threads for write operations in InnoDB. The default value is 4. We set it to 32.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_write_io_threads
innodb_buffer_pool_size
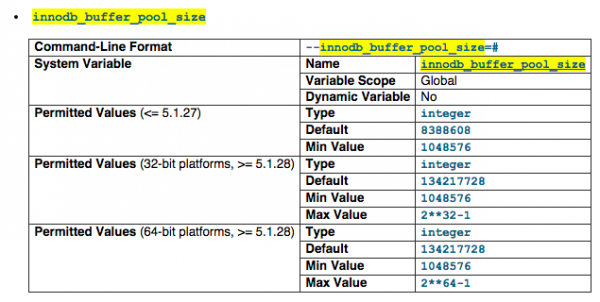
The size in bytes of the memory buffer InnoDB uses to cache data and indexes of its tables. The larger you set this value, the less disk I/O is needed to access data in tables. On a dedicated database server, you may set this to up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. But you most likely won't be able to set to 80%, in our case, we just set it to 400M. (it can goes up to few GB but that depends on your mysqltuner advises would be better)
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_buffer_pool_size
innodb_file_per_table
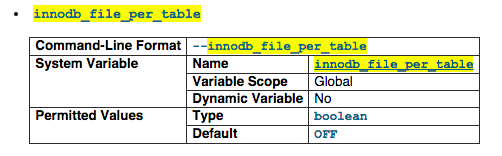
If innodb_file_per_table is disabled (the default), InnoDB creates tables in the system tablespace. If innodb_file_per_table is enabled, InnoDB creates each new table using its own .ibd file for storing data and indexes, rather than in the system tablespace. This is to prevet shits from happening.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_file_per_table
innodb_stats_on_metadata
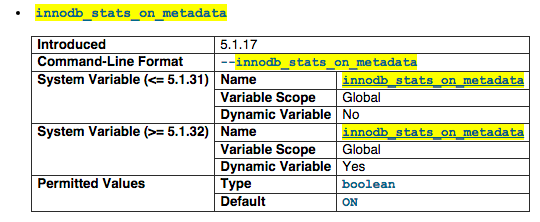
When this variable is enabled (which is the default, as before the variable was created), InnoDB updates statistics during metadata statements such as SHOW TABLE STATUS or SHOW INDEX, or when accessing the INFORMATION_SCHEMA tables TABLES or STATISTICS. This is a bitch when you have a lot of InnoDB which will keep updating the statics and may cause your simple SQL to runs for more than 10-50 seconds.
For more information visit http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/innodb-parameters.html#sysvar_innodb_stats_on_metadata


